Characterization of composite materials requires a range of tests under different loading conditions e.g. tension, compression, shear, flexure and peel. Instron provides a range of, high-performance, Composites Testing fixtures which conform to the requirements of the appropriate ASTM, ISO, EN and other testing standards.
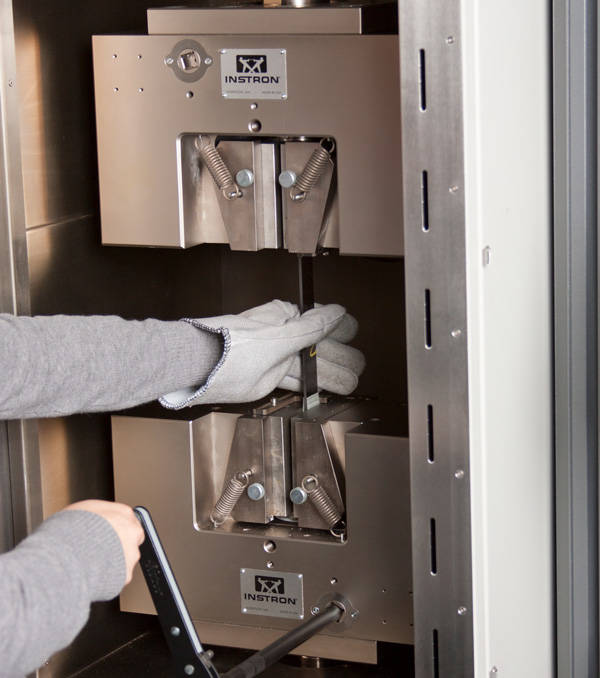

Composites Tension Testing Grips
Both manual and hydraulic grip types capable of operating over a wide range of temperatures are available. Moving body manual and hydraulic wedge grips are recommended for testing composite materials as they provide reliable gripping of test specimens whilst maintaining accurate and repeatable alignment meeting Nadcap requirements for aerospace testing. Adapters are available to allow a range of composites test fixtures to be attached to these grips meaning that the grips do not have to be removed when changing test set ups, minimizing disruption and enhancing productivity.
More Info
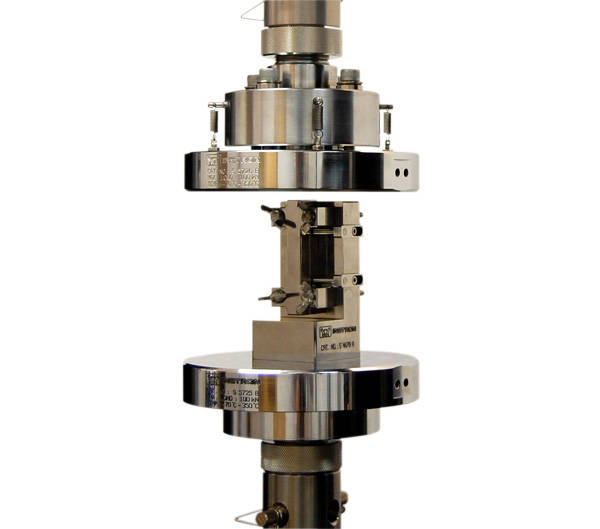

Composites Compression Test Fixtures
Supported Gauge Section.
The anti-buckling fixture was originally designed for the compression testing of rigid plastics per ASTM D695 and the shear testing of reinforced plastics per ASTM D3846. Boeing then adapted the fixture for use with high strength composites, introducing an L-shaped base support to ensure accurate and consistent alignment of the fixture and specimen. The SACMA standard followed the Boeing design with an added alternative support fixture with a cutout, allowing bonded strain gauges to be used at the center of the specimen for precise strain measurement.
More Info
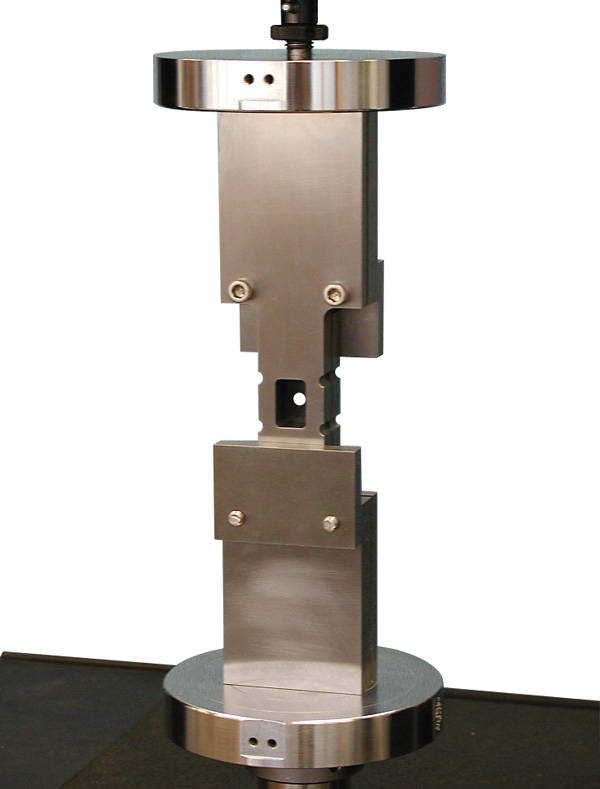

Composites Compression Test Fixtures
Unsupported Gauge Section.
Compression testing of composites without anti-buckling guide plates is often preferred as the free unsupported length is more representative of true compression behavior. Three fixtures are available: IITRI, Wyoming Modified Celanese, and Combined Loading Compression (CLC).
More Info
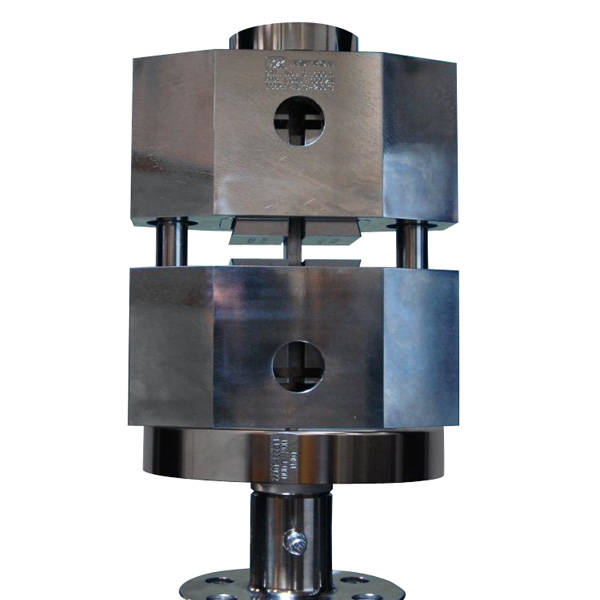

Composites Compression Test Fixtures
Boeing Open Hole Compression Fixture.
The ASTM D6484 / D6484M fixture is used to perform open-hole compressive tests on multi-directional polymer matrix composite laminates reinforced with high modulus fibers. The open-hole compression fixture was originally developed by Boeing and is outlined in Boeing specification BSS 7260. The test specimen is rectangular with a central hole. The fixture consists of a pair of interlocking plates that guide and prevent the specimen from buckling under the applied compressive load.
More Info
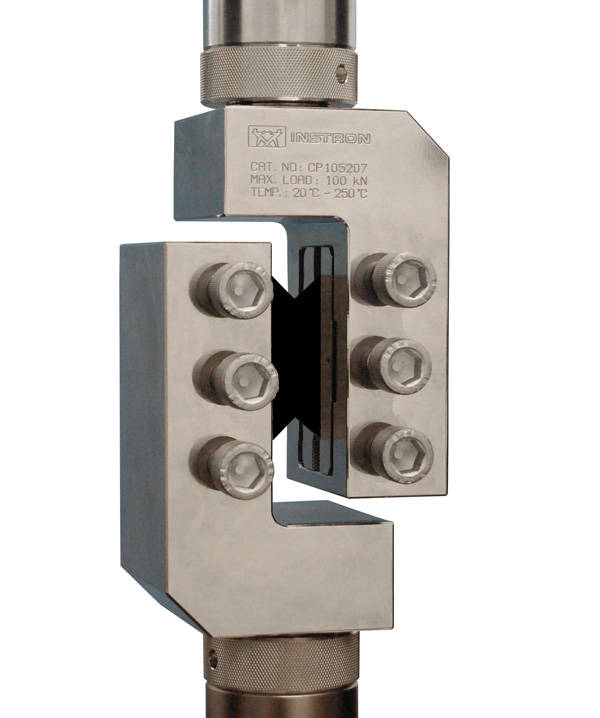
Composites V-Notch Shear Test Fixtures
Instron Shear Test Fixtures are designed for in-plane or interlaminar shear testing of composite materials. The V-Notched Beam Method, or more commonly known as the Iosipescu Shear Method, was standardized into ASTM D5379 in 1993, while the V-Notched Rail Shear Method was more recently introduced in 2005 under ASTM D7078. Both test methods share many common characteristics and have the distinctive V-notches in the specimen design, which serve to create a localized and approximate uniform shear stress zone between the notches. It’s important to note that the two fixtures in ASTM D7078 and D5379 are quite different in their specimen design, the way in which load is applied to the specimen and consequently, the type of results obtained.
More Info

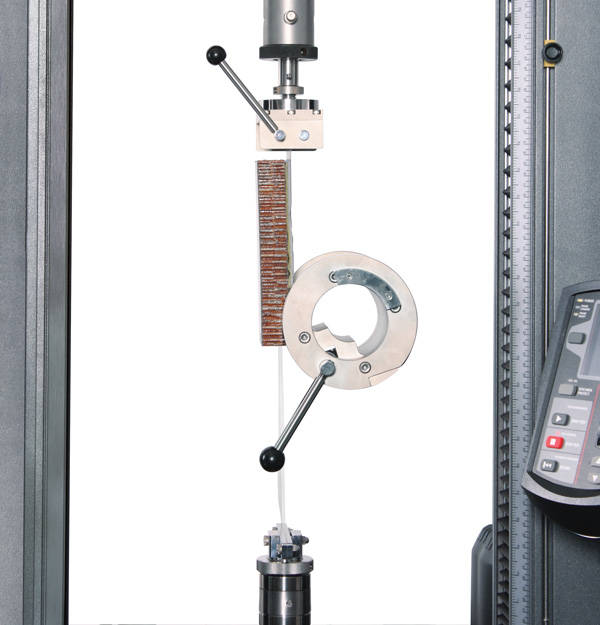
Composites Rail Shear to ASTM C273
ASTM D4255 describes both 2 Rail and 3 rail methods of determining the in-plane shear strength of a composite laminate panel. In the 2 Rail test (Method A) a laminate panel specimen is clamped between loading plates and yokes and then subject to shear loading. Measurement of shear strain requires the use of strain gauges on the specimen. Two types of fixture are available: one working in a compression mode and one working in a tension mode. A specimen template is included to ensure the accurate location of the holes in the specimen.
More Info
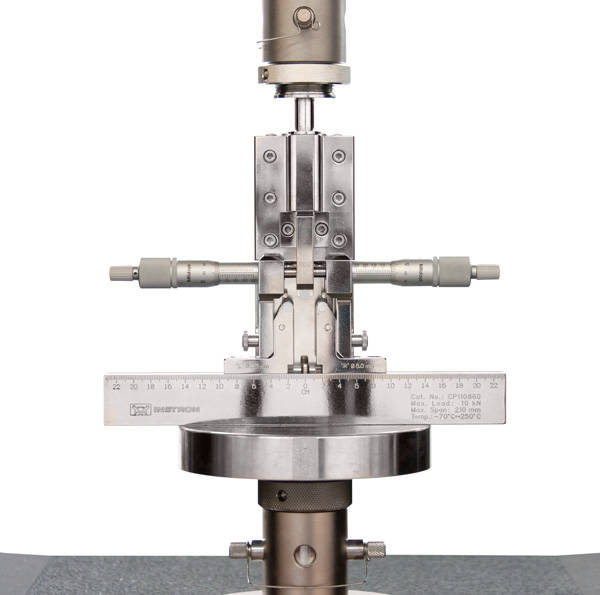
Flexural and Interlaminar Shear Bend Fixture
A modular fixture for flexural and Interlaminar Shear Strength (ILSS) testing to a wide range of standards. Capable of operation from -70 to +250 deg C (-94 to +482 deg F).
More Info
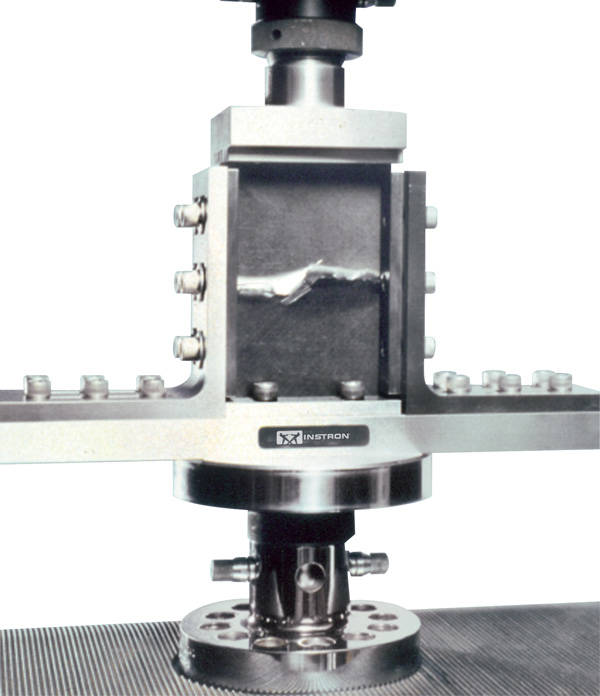

Compression After Impact
“Boeing CAI” Fixture.
The “Boeing CAI” fixture is used to test the impact resistance of carbon and other fiber-reinforced polymer composite laminates. These materials are prone to great reduction in compressive strength, even when the impact load is insufficient to cause visible damage. The post-impact compression test is used to assess the relative performance of different composite laminates with different fiber matrix combinations. Laminates are subjected to low-velocity impact loading simulating tool drops and flying debris or may be subjected to an out-of-plane static indentation (ASTM D6264 / D6264M). Specimens then undergo a compression after impact (CAI) test on an electromechanical or servo hydraulic testing machine.
More Info
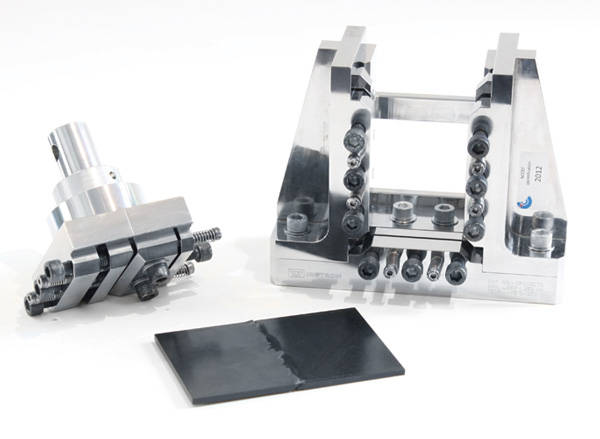

Compression After Impact
Airbus AITM 1-0010.
The “Airbus CAI” fixture is used to test the impact resistance of carbon and other fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP) composite laminates. These materials are prone to great reduction in compressive strength even when the impact load is insufficient to cause visible damage. The post-impact compression test is used widely to assess the relative performance of different composite laminates with different fiber matrix combinations. In the first part of the test the laminates are subjected to low-velocity impact loading simulating tool drops and flying debris. Specimens then undergo a compression after impact (CAI) test on an electromechanical or servo hydraulic testing machine.
More Info
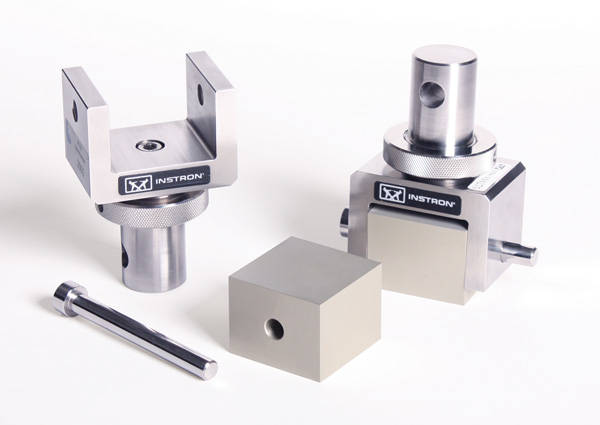

Sandwich Constructions Flatwise Tension Test Fixtures
ASTM C297 describes a method of determining the bond strength between the facing and core of a sandwich core panel or the strength of the core itself, if the bond strength between the facing and the core is sufficiently strong. The specimen is bonded to thick loading blocks and then subject to tensile loading applied via the blocks. Each half of the test fixture incorporates a dual flexible yoke to ensure that pure axial load is applied to the specimen. The fixture can be used to test a variety of different sandwich core materials including honeycomb core structures and continuous core structures, such as foam or balsa wood.
More Info

Sandwich Constructions
Flatwise Shear to ASTM C273.
ASTM C273 describes a method of determining the shear strength of a sandwich core panel. The test the specimen is bonded to thick loading plate blocks and is subject to shear loading applied via the blocks. Two types of fixture are available: one working in a tension mode and one working in a compression mode. Both fixtures are supplied with carbon steel loading blocks. Either fixture can test a variety of different sandwich core materials including honeycomb core structures and continuous core structures, such as foam or balsa wood.
More Info

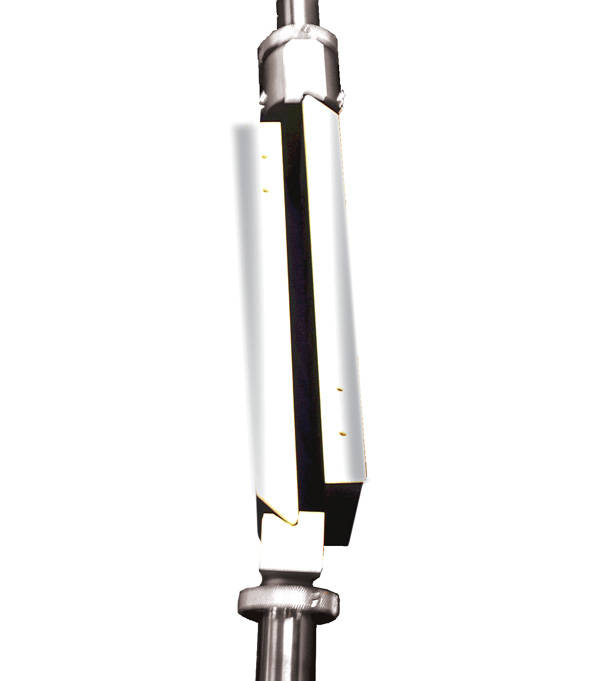
Climbing Drum Peel Fixture
The Climbing Drum peel test for adhesives measures the strength of the adhesive bond between the core and the facing of a honeycomb panel.
More Info

Strain Gauge Adapters for 120 and 350 ohm Gauges
From aerospace to construction, strain gauges are used in a variety of industries to measure strain in both materials and structural testing. These strain gauge adapters allow a single strain gauge to be used with any standard Instron strain channel. The strain gauge adapter contains bridge completion resistors and electrical calibration circuitry. The strain gauge leads are connected to the adapter via a spring-loaded terminal. Both 2 and 3 wire strain gauge connections are supported. The adapter is compatible with strain gauges that have gauge factors between 1.5 – 2.5. Multiple strain gauges require multiple adapters, which can be used up to the maximum number of strain channels fitted to the testing machine.
More Info
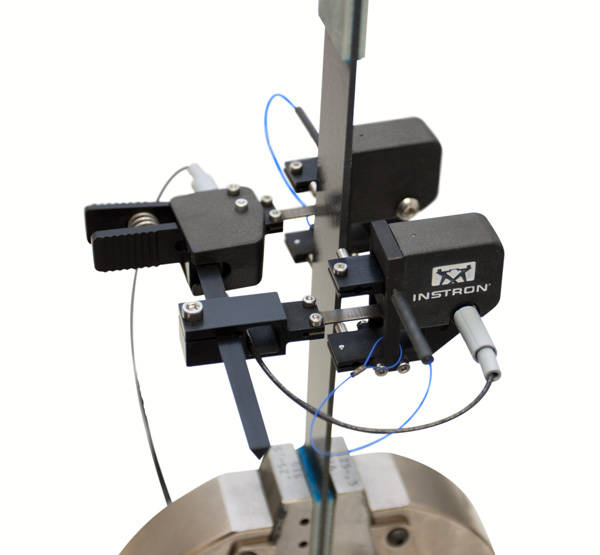

Biaxial Extensometer
A range of Bi-axial and Averaging Axial extensometers are optimized for measuring strain when testing composites. These extensometers feature simple, single- handed operation and incorporate automatic electrical calibration and transducer recognition including a unique digital serial number. All of the extensometers measure the axial strain on both sides of the specimen. The use of average axial strain corrects for any specimen bending due to mis-alignment for the consistent and accurate determination of modulus. Biaxial versions measure transverse strain allowing for the determination of Poisson’s Ratio and In-Plane Shear strain.
More Info
